SysAdmin Notes¶
Initial notes about debian operating system
Create new user¶
sudo useradd -m -c "The Allmigthy" ambagasdowa -s /bin/bash
Installing sudo¶
apt install sudo
Then add to sudoers group
/sbin/adduser USERNAME sudo
Or :
usermod -aG sudo USERNAME
usermod -aG tty,dialup,video,audio USERNAME
Configuration overview¶
Now, if you want to allow certain users to execute certain programs, here’s a quick example (for more information, read the fine manual), which you can put in a file in /etc/sudoers.d, probably using visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/myfile.
No password prompt for sudo user¶
If you want sudo group members to execute commands without password, add the line:
%sudo ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
#or by user
my_user ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Examples
# User
root ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
myself ALL=(ALL:ALL) NOPASSWD:/bin/apt update, PASSWD:/bin/apt install*
# Groups
%sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
Code Snippets¶
1 2 3 | |
Scan Network¶
CIDR Network notation can be calculate with ipcal
Note
Classless Inter-Domain Routing CIDR
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
How to Scan Networks with Nmap¶
sudo nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
ambagasdowa@Kalacmul:~$ nmap -sn 192.168.1.0/24
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2023-08-06 09:51 CST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.62
Host is up (0.078s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.85
Host is up (0.021s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.87
Host is up (0.0025s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.99
Host is up (0.00088s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.113
Host is up (0.19s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.114
Host is up (0.049s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.128
Host is up (0.11s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.129
Host is up (0.37s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.168
Host is up (0.10s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.178
Host is up (0.25s latency).
Nmap scan report for Kalacmul.uruk (192.168.1.224)
Host is up (0.000079s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.248
Host is up (0.13s latency).
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.254
Host is up (0.0011s latency).
Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (13 hosts up) scanned in 14.50 seconds
Fing¶
wget https://www.fing.com/images/uploads/general/CLI_Linux_Debian_5.5.2.zip
sudo fing 192.168.1.0\24
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| State | Host | MAC Address | Last change |
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| UP | 192.168.1.62 | CA:39:7B:D9:2A:40 | 09:58:08 |
| UP | 192.168.1.69 | 54:92:09:6C:A0:1F | 09:58:08 |
| UP | 192.168.1.85 | B4:E6:2D:6C:F0:3F | 09:58:09 |
| UP | 192.168.1.87 | D8:BF:C0:EC:A1:69 | 09:58:09 |
| UP | 192.168.1.99 | E4:C3:2A:1B:AD:68 | 09:58:08 |
| UP | 192.168.1.113 | 10:D5:61:64:6F:3E | 09:58:09 |
| UP | 192.168.1.114 | 9C:1C:37:0B:3B:F8 | 09:58:09 |
| UP | 192.168.1.128 | 68:57:2D:AA:2F:57 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.129 | 10:D5:61:67:12:94 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.131 | A2:F5:09:FF:EB:C9 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.168 | 10:D5:61:69:F5:F6 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.170 | 10:D5:61:6F:41:D5 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.176 | 38:1F:8D:CA:D7:A3 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.178 | 94:D3:31:3E:84:C6 | 09:58:10 |
| UP | 192.168.1.224 | FC:4D:D4:D1:A6:97 | 09:58:07 |
| UP | 192.168.1.248 | 32:CA:0B:36:56:E0 | 09:58:12 |
| UP | 192.168.1.254 | 78:B4:6A:8C:58:E9 | 09:52:12 |
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
09:58:24 > Discovery round completed in 18.201 seconds.
09:58:24 > Network 192.168.1.0/24 has 203/17 hosts up.
CHD¶
CHD is a lossless compression format originally developed for MAME, for
the hard-drive contents of certain arcade machines. It has since been
used in several other emulators as a means of storing CD-ROM game data.
For CD-based games, it compresses the contents of a disc image (.cue
+ .bin files) to a single .chd file.
Creating CHDs from CD-ROMs¶
.chd file from an
existing .cue is performed by running:chdman createcd -i <game.cue> -o <game.chd>
To compress every file in a directory, use:
cd /path/to/folder
for i in *.cue; do chdman createcd -i "$i" -o "${i%.*}.chd"; done
To compress every file in subdirectories within a folder, use:
cd /path/to/folder
for i in */*.cue; do chdman createcd -i "$i" -o "${i%.*}.chd"; done
Windows¶
The following archive contains a MAME 0.205 version of CHDMAN and Windows batch files that can be used to quickly convert your PSX games to CHD (V5): Download
Run the appropriate batch file in the same folder as the ROM(s) you wish
to compress, and it will search subfolders for .cue files to
compress. If a .chd is not generated after running the appropriate
batch, then something is wrong with the ROM(s) .cue.
MacOS¶
In MacOS, chdman can be installed through
Homebrew, with the following command:
brew install rom-tools
Linux¶
On Debian based systems, including RetroPie, chdman can be found in
the mame-tools package and can be installed with:
sudo apt install -y --no-install-recommends mame-tools
Interesting Commands¶
Timezone¶
To view all available time zones
1 | |
To set a time zone
1 | |
Progress bar¶
If you have a large collection of files or just very big files this command assembly is is pretty handy as it gets you a progress bar:
$ pv files.zip= | cat - > uberFile.zip
25.0GiB 0:50:24 [8.48MiB/s] [============================================================>] 100%
$ unzip uberFile.zip
Ethernet¶
The ethtool -s command can be used to change the current settings by defining the values for speed, duplex, and autoneg in the following format:
sudo ethtool -s [device_name] autoneg [on/off] speed [10/100/1000] duplex [half/full]
For example, to set the speed at 1000Mb/s, the duplex mode to full and the auto-negotiation to on the command would be:
sudo ethtool -s enp0s3 autoneg on speed 1000 duplex full
The ethtool [device_name] command is necessary to confirm that the changes have been applied.
SC-IM¶
Install dependencies on debian
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt install bison flex autoconf automake gettext libtool autoconf-archive \
cutils gnuplot python3-xlsxwriter libxml2-dev libzip-dev xlsx2csv libxlsxwriter-dev \
libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev libzip-dev bison lua5.1 liblua5.1-dev liblua5.4-0-dbg \
libgnuplot-iostream-dev
sudo apt install liblua5.1*
# OR
sudo apt install liblua5.1-json liblua5.1-0 liblua5.1-dev liblua5.1-bitop0 liblua5.1-leg-dev liblua5.1-0-dbg liblua5.1-0-dev liblua5.1-luacsnd-dev liblua5.1-rrd0 liblua5.1-bitop-dev liblua5.1-rrd-dev liblua5.1-luacsnd
Checking libs exits¶ambagasdowa@balam:~$ llt /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/lua/5.1/
Permissions Size User Group Date Modified Name
drwxr-xr-x - root root 7 Aug 13:51 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/lua/5.1
drwxr-xr-x - root root 7 Aug 13:50 ├── mime
lrwxrwxrwx 32 root root 23 Mar 2023 │ └── core.so -> ../../../liblua5.1-mime.so.2.0.0
drwxr-xr-x - root root 7 Aug 13:50 ├── socket
lrwxrwxrwx 34 root root 23 Mar 2023 │ ├── core.so -> ../../../liblua5.1-socket.so.2.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 41 root root 23 Mar 2023 │ ├── serial.so -> ../../../liblua5.1-socket-serial.so.0.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 39 root root 23 Mar 2023 │ └── unix.so -> ../../../liblua5.1-socket-unix.so.2.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 30 root root 27 Jan 2023 ├── bit.so -> ../../liblua5.1-bitop.so.0.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 35 root root 10 Dec 2022 ├── lfs.so -> ../../liblua5.1-filesystem.so.0.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 29 root root 27 Jul 2022 ├── lpeg.so -> ../../liblua5.1-lpeg.so.2.0.0
.rw-r--r-- 1.0M root root 24 Nov 2022 ├── luaCsnd6.so
lrwxrwxrwx 28 root root 31 Jan 2023 ├── rrd.so -> ../../liblua5.1-rrd.so.0.0.0
lrwxrwxrwx 28 root root 10 Dec 2022 └── ssl.so -> ../../liblua5.1-sec.so.1.0.0
Compile libxls on Debian
clone lib
git clone https://github.com/libxls/libxls
Compile
./autogen.sh
./configure
make
make install
In sc-im source
make -C src
sudo make -C src install
For copy to system clipboard
ccopy
ccpaste
Install luarocks¶
sudo apt install luarocks
Install some libs for running hbues production spreedsheets
luarocks --local install lunajson
luarocks --local install date
OrangePi¶
Installation¶
Both the Panfrost and Lima drivers are included in Mesa and should work out-of-the-box after installing the relevant packages (which are, in practice, libglx-mesa0 and libgl1-mesa-dri).
OpenCL support is not implemented yet. Hardware video acceleration is not within the scope of the Panfrost or Lima drivers.
Troubleshooting¶
No video/GPU acceleration
If you see Couldn’t initialize GPU devfreq in the log files, then you’re running into the problem that a devfreq module wasn’t loaded (early enough). Try (as root or with sudo) if rmmod panfrost && modprobe governor_simpleondemand && modprobe panfrost fixes the problem. If it does, then add governor_simpleondemand to the initramfs modules and rebuild the initramfs.
You can do that as root (or with sudo) as follows:
echo governor_simpleondemand >> /etc/initramfs-tools/modules && update-initramfs -u -k $(uname -r)
How to enable 3d support in zero3
GPU is not enabled in the current builds be they 5.4 or 6.1 based, but you can enable it by editing the dtb.
# Edit the dts file
dtc -I dtb -O dts /boot/dtb/allwinner/sun50i-h616-orangepi-zero3.dtb >/tmp/op3.dts
# open /tmp/op3.dts with your favourite editor
# search for 'mali'
# in the section where you find it edit the line status='disabled' to status='okay'
# recompile
dtc -I dts -O dtb /tmp/op3.dts >zero3.dtb
# Then replace the original with this after backing up and reboot.
# glxinfo should then show the panfrost driver in action.
Python¶
To easiest way to get back the old pre-Debian12 behaviour just for your user, is to add break-system-packages = true in the [global] section of your ~/.config/pip/pip.conf, as noted in /usr/share/doc/python3.11/README.venv:
This can be overriden by passing the –break-system-packages option to pip. You do this at your own risk: pip may break Python modules that part of your Debian system depends on. This option can also be specified by exporting PIP_BREAK_SYSTEM_PACKAGES=1 or configuring the following in ~/.config/pip/pip.conf or /etc/pip.conf:
[global]
break-system-packages = true
OR
sudo rm /usr/lib/python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED
Merge multiple dirs in one simlink¶
You can install unionfs-fuse for this: .. code-block:: bash
sudo apt-get install unionfs-fuse
Mounting:
unionfs-fuse /folder1=RW:/folder2=RW /mount/point
It will group all content from folder1 and folder2 (or more if you want) to your mount point
Umounting:
sudo umount /mount/point
For example for mame roms
unionfs-fuse -o allow_other,use_ino,suid,dev,nonempty /media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ ROMs\ \(bios-devices\)/=RO:/media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ ROMs\ \(merged\)/=RO:/media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ CHDs\ \(merged\)/=RO arcade
Scraper¶
Directories in Emulation Station :
downloaded_media/
└── arcade
├── backcovers
├── covers
├── fanart
├── marquees
├── miximages
├── screenshots
└── titlescreens
The Relation is
├── backcovers ?
├── covers fly
├── fanart b
├── marquees m
├── miximages mix4,mix3,3b,b
├── screenshots s
└── titlescreens t
scraper -mame -mame_img "fly" -mame_src "gdb,adb,mamedb,ss" -image_dir ~/.emulationstation/downloaded_media/arcade/covers -image_suffix "" -img_format png -rom_dir /media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ ROMs\ \(merged\)/
scraper -ss_password `/usr/bin/cat $HOME/credentials/ss/password` -ss_user `/usr/bin/cat $HOME/credentials/ss/usr` -mame -console_src "ss,gdb,ovgdb,adb,mamedb" -console_img "mix3,mix4,3b,b,s,l,f,a,fly,t,m,c" -image_dir ~/.emulationstation/downloaded_media/arcade/covers/ -image_suffix "" -img_format png -rom_dir /media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ ROMs\ \(merged\)/
Skyscraper -f emulationstation -p arcade -u user:pass -i /media/source/torrents/end/MAME\ 0.261\ ROMs\ \(merged\)/ -g /home/ambagasdowa/.emulationstation/downloaded_media/arcade -o /home/ambagasdowa/.emulationstation/downloaded_media/arcade -s screenscraper -t 2
Skyscraper modules
screenscraperarcadedbthegamesdbopenretromobygames
gathering phase¶1 | |
gamelist genertation phase¶1 | |
Torrents¶
Install we-get
python3 -m pip install --user git+https://github.com/rachmadaniHaryono/we-get.git
Search torrents with we-get
we-get --search="roms" --target the_pirate_bay,1337x,limetorrents,il_corsaro_nero,eztv,yts -n 300
Install aria2
sudo apt install aria2
config example
~/.config/aria2/aria2.conf¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | |
Aria2 as daemon¶
~/.config/systemd/user/aria2cd.service¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
run the daemon
aria2c --enable-rpc --rpc-secret *** --dir ~/torrents/ --enable-dht=true
Restart the service
systemctl --user restart aria2cd.service
Install aria2p
python3 -m pip install aria2p[tui]
add Magnet with aria2p
aria2p --secret *** add "magnet:?xt=urn:btih:E9E403A06D08CA0FEC40BBC32AB2BDE5B51782BF..."
Whatch them
aria2p --secret *** top
Fetch monitors¶
TODO: Awesome Fetchs
neofetch
cpufetch
onefetch
Update OneFetch¶
cargo install onefetch --force
TIP: What is the meaning of USB DM?
The data pair in USB is differential. It is just normal practice to call the (-) side Data Minus (DM) and the (+) side Data Plus (DP).
Testing MPV¶
startx /usr/bin/mpv --fs filename.mp4 -- :1
WSDD¶
sudo apt install wsdd
Read¶
Extract a content in file and put in vim buffer
:r! sed -n 147,227p /path/to/foo/foo.c
For example
1 | |
:put =readfile('/path/to/foo/foo.c')[146:226]
"I just had to do this in a code project of mine and did it this way:
"In buffer with /path/to/foo/foo.c open:
:147,227w export.txt
"In buffer I'm working with:
:r export.txt
PDF to Image¶
You can use pdftoppm from the poppler-utils package to convert a
PDF to a PNG:
pdftoppm input.pdf outputname -png
This will output each page in the PDF using the format
outputname-01.png, with 01 being the index of the page.
Converting a single page or a range of pages of the PDF¶
pdftoppm input.pdf outputname -png -f {page} -singlefile
Change {page} to the page number. It’s indexed at 1, so -f 1
would be the first page.
If you’d like to work on a range of pages, you can also specify a number
for the flag -l (last page), so having -f 1 -l 30 would specify
the pages from 1 to 30.
Note again that .png will be appended to outputname
automatically, so there’s no need to include the extension. Also,
-singlefile removes the -01 suffix cited above, since the output
is known to have only one file.
Specifying the converted image’s resolution¶
The default resolution for this command is 150 DPI. Increasing it will result in both a larger file size and more detail.
To increase the resolution of the converted PDF, add the options
-rx {resolution} and -ry {resolution}. For example:
pdftoppm input.pdf outputname -png -rx 300 -ry 300
You can use ImageMagick for this. Note that newer versions of ImageMagick have disabled the ability to convert PDF files to images, because of security vulnerabilities that are being exploited in the wild. See the comments for more details and for a workaround.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
Whereby:
PNG, JPG or (virtually) any other image format can be chosen.
-density xxx will set the DPI to xxx (common are 150 and 300).
-quality xxx will set the compression to xxx for PNG, JPG and MIFF file formates (100 means no compression).
[666] will convert only the 667th page to PNG (zero-based numbering so [0] is the 1st page).
All other options (such as trimming, grayscale, etc.) can be viewed on the website of Image Magic.
Zathura¶
Make zathura the default pdf viewer
Ensures, for example, that xdg-open(1) will open pdf files with zathura.
First, ensure a desktop
entry for zathura
exists at /usr/share/applications/org.pwmt.zathura.desktop. If it
does not, download the desktop entry from from the zathura
repo
to /usr/share/applications/org.pwmt.zathura.desktop.
Then, set zathura as default using xdg-mime(1)
$ xdg-mime default org.pwmt.zathura.desktop application/pdf
XDG-Desktop¶
To find out the default app for a particular type of file¶
xdg-mime query filetype Documents/test.pdf
application/pdf
To find out the mime for the extension¶
xdg-mime query default application/pdf
# Response:
okularApplication_pdf.desktop
to set default app for an mimetype¶
xdg-mime default zathura.desktop application/pdf
to test if applied successfully¶
xdg-open test.md
kitty Terminal¶
1 | |
Printers¶
sudo apt install printer-driver-cups-pdf
list printers¶
lpstat -v
1 2 3 4 | |
or
lpstat -p -d
1 2 3 4 5 | |
lp -d PDF -P 105 file.pdf
Set default printer
lpoptions -d MFP137
Add Printer
sudo lpinfo -v
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
sudo lpadmin -p SUPERRISC_S31 -D "Receipt Printer" -E -v usb://SUPERRISC/S31
printer DCP-1510 disabled since Tue 02 May 2023 05:55:18 PM CST - Unplugged or turned off
printer HP040E3C84624F_HP_Laser_MFP_131_133_135_138_ is idle. enabled since Wed 14 Feb 2024 08:32:40 AM CST
printer MFP137 is idle. enabled since Wed 14 Feb 2024 05:15:25 PM CST
printer PDF is idle. enabled since Wed 07 Feb 2024 01:42:03 PM CST
printer SUPERRISC_S31 is idle. enabled since Wed 14 Feb 2024 05:43:35 PM CST
system default destination: MFP137
FZF test¶
Workig code for search pattern inside a pdf
find "$1" -type f -iname "*.pdf" | xargs -d '\n' -I {} pdfgrep -H -n "$scrapePattern" {} | fzf --multi --cycle --prompt='▶ ' --pointer='→ ' --marker='✓ ' --layout 'reverse' | eval $(awk -F : '{ print "pdftotext -f "$2" -l "$2 " -layout \""$1"\" -" }') | cat -p --paging=never
# and for capture a image
find "$1" -iname '*.pdf' | xargs -d '\n' -I {} pdfgrep -H -n "$scrapePattern" {} |fzf --multi --cycle --prompt='▶ ' --pointer='→ ' --marker='✓ ' | eval $(awk -F : '{ print "pdftoppm -f "$2" -l "$2 " -png \""$1"\" /tmp/img" }') && imv-x11 -r -d /tmp/img-*.png
Find¶
Recursively find and replace in files
find . -type f -name "*.txt" -print0 | xargs -0 sed -i '' -e 's/foo/bar/g'
Whit fzf¶
find ./ -type f | xargs -d '\n' -I {} egrep --color -H 'pattern' {} | fzf --multi --cycle --prompt='▶ ' --pointer='→ ' --marker='✓ ' --layout 'reverse'
Find and replace¶
find docs/ -type f | xargs -d '\n' -I {} egrep -H --color "imscholar" {} \\
| fzf --multi --cycle --prompt='▶ ' --pointer='→ ' --marker='✓ ' \\
| eval $(awk -F: '{print "sed -i '' 's/imscholar/portalapps/g' "$1""}' )
Consulta RFC¶
Consulta CURP¶
Update Letsencrypt
sudo certbot renew
Add Certificates
certbot --nginx -d baizabal.xyz -d portaltms.com -d office.baizabal.xyz -d video.baizabal.xyz -d voip.baizabal.xyz -d time.baizabal.xyz -d music.baizabal.xyz -d portalapps.xyz -d radiobases.com -d tiamandados.com --post-hook "/usr/sbin/service nginx restart"
Audio & Video Stream¶
Convert RTSP stream to virtual web camera¶
You can easily do it on Ubuntu, Debian, Raspian, and Ubuntu Linux for Windows subsystems using the following method,
Installing required libraries, v4l2loopback-dkms and ffmpeg:
sudo apt install v4l2loopback-dkms
sudo apt install ffmpeg
Emulate a video device:
sudo modprobe v4l2loopback card_label="Webcam Stream Name" exclusive_caps=1
Streaming from RTSP uri to the created virtual device:
ffmpeg -stream_loop -1 -re -i rtsp://uri -vcodec rawvideo -threads 0 -f v4l2 /dev/video0
You can replace the ‘0’ at the end of /dev/video0 with the number of
the available and playable video device.
a better example
ffmpeg -stream_loop -1 -re -i rtsp://uri -vcodec rawvideo -threads 0 -pix_fmt yuv420p -preset ultrafast -b:v 600k -f v4l2 /dev/video0
Capture RTSP stream from IP Camera and store¶
ffmpeg -i rtsp://192.168.0.21:554/mpeg4 -vcodec copy -acodec copy -map 0 -f segment -segment_time 300 -segment_format mp4 "ffmpeg_capture-%03d.mp4"
Retransmision¶
ffmpeg -i rtsp://original-source \
-pix_fmt yuv420p -c:v libx264 -preset ultrafast -b:v 600k \
-c:a aac -b:a 160k \
-f rtsp rtsp://localhost:8554/mystream
Mediaplayer¶
creating a virtual microphone and streaming audio into it from RTSP IP camera¶
I need to create both virtual webcam and virtual microphone on an Ubuntu 16.04 machine for use in web application using WebRTC through my web browser.
I need to feed video and audio to these 2 virtual devices from an IP camera (RTSP stream). Playing RTSP stream directly in VLC works fine with both video and audio.
For this, I have created a /dev/video1 with video4linux2. I am able to feed the IP camera to /dev/video1.
ffmpeg -i rtsp://ip_address:554/streaming/channels/101/ -f v4l2 /dev/video1
If I look in VLC player, I can select /dev/video1 as a video device, but I have only “hw:0,0” as audio device, which is my in-built microphone.
How to properly feed such RTSP stream to both virtual webcam and virtual microphone?
You need some sort of loopback audio driver. If you want to do this at
the Alsa level, you can lose the snd-aloop module.
https://www.alsa-project.org/main/index.php/Matrix:Module-aloop#aloop_driver
If your intended destination supports Pulseaudio, you can add a null sink and use its monitor source to record from it.
pactl load-module module-null-sink sink_name=video1
The monitor source is then named video1.source.
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/PulseAudio/Examples
Then, you need to add an additional output from FFmpeg. That might be as
simple as adding something like -f pulse "video1" to the end of what
you have now
Note
When I add -f pulse “video1”, the sound is played through my speakers directly (Monitor of Built-in Audio Analog Stereo) instead of the virtual microphone, maybe you have an idea why? Here is the command I used to play the sound through the ALSA virtual microphone: ffmpeg -re -i webcam_record.mp4 -f v4l2 /dev/video0 -f alsa hw:1,1. When I tested the result with VLC it did not work, I had to test with guvcview.
My goal is testing Video Room Application, so I’m going to create multiple virtual machines with virtual webcams and microphones.
Webcam is working fine with v4l2loopback, but microphone is not.
I’m trying to use ALSA.
ffmpeg -re -i cox.mp4 -map 0:0 -f v4l2 /dev/video0 -map 0:1 -f alsa hw:1
As a result, Firefox sees Dummy Video device and can use it. Firefox
also sees Dummy analog stereo and Loopback analog stereo, but
there is no sound from these ‘microphones’.
Something wrong with ffmpeg command or with ALSA itself or I’m just doing everything wrong?
Note
Thanks for the hint -f alsa hw:1, I managed to get it working by
using -f alsa hw:1,1 instead. First, I had to enable the virtual
microphone with modprobe snd-aloop (see this related question
stackoverflow.com/a/43565890/1176454).
Here is the full command I used:
ffmpeg -re -i webcam_record.mp4 -f v4l2 /dev/video0 -f alsa hw:1,1.
I then tested to play the fake webcam and microphone stream with VLC but
it did not work. When I tried with guvcview it worked.
SSH¶
SSH notes
Generate Public keys¶
You can generate a new SSH key on your local machine. After you generate the key, you can add the public key to your account on GitHub.com or your own server to enable authentication for Git or Server operations over SSH.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Adding your SSH key to the ssh-agent¶
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
Add your SSH private key to the ssh-agent¶
If you created your key with a different name, or if you are adding an existing key that has a different name, replace id_ed25519 in the command with the name of your private key file.
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
Upload Public key to Server¶
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub -p 22 user@1.1.1.1
# OR
ssh-copy-id user@server.com
Configure ssh to use the key.
vim ~/.ssh/config
Your config file should have something similar to the following:
Host SERVERNAME
Hostname ip-or-domain-of-server
User USERNAME
PubKeyAuthentication yes
IdentityFile ./path/to/key
For example
config file example¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |
Check that you are connecting to the correct server¶
ssh -vT git@github.com
Check logs in /var/log/auth.log
Disable password authentication¶
Most servers allow both username/password authentication and SSH key authentication, but if you want to allow only SSH key authentication, then you can disable the use of usernames and passwords. Be certain that you have thought through the ramifications before doing so, because once you take this action, successful certificate authentication will be the only way to access your server.
This is accomplished through the sshd_config file. The exact location of this file varies by Linux distribution. Often it’s in the /etc/ssh directory. Edit this file to include the following parameters:
/etc/ssh/ssh_config¶1 2 3 | |
After change reload the server
sudo systemctl restart sshd.service
SSH Authentication Refused: Bad Ownership or Modes for Directory¶
check this permissions
SSH doesn’t like it if your home or ~/.ssh directories have group write permissions. Your home directory should be writable only by you, ~/.ssh should be 700, and authorized_keys should be 600 :
chmod go-w ~/
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Run Commands over ssh¶
Count files in remote¶1 | |
1 | |
ssh user@example.com tail -f /var/log/apache2/access.log | logstalgia --sync
ssh -t ambagasdowa@baizabal.xyz "sudo /bin/cat /var/log/nginx/access.log" >> access_baizabal.log && logstalgia 1280x720 -x -s .70 -p 5 access_baizabal.log -o - | ffmpeg -y -r 60 -f image2pipe -vcodec ppm -i - -vcodec libx264 -preset ultrafast -crf 1 -threads 0 -bf 0 /media/White/box/VideoManual/log/logstalgia_today.mp4
ssh -t ambagasdowa@baizabal.xyz "sshpass -p password sudo /usr/bin/tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log" | logstalgia --sync -x -s .30 -p 2
ssh -t ambagasdowa@baizabal.xyz "sshpass -p password sudo /usr/bin/tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log" | logstalgia --sync -x -s .30 -p 2 -o - | ffmpeg -y -r 60 -f image2pipe -vcodec ppm -i - -vcodec libx264 -preset ultrafast -crf 1 -threads 0 -bf 0 /media/White/box/VideoManual/log/logstalgia_live.mp4
Real Example about remote command over ssh
Update remote repo and compile login with pub-key¶1 | |
Note
Simplify commands
add in ~/.bash_alias
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | |
then update bash exec bash
upbzbweb "commit-message"
Nextcloud Analitics update data source example¶ssh -t baizabal.xyz -- 'sudo -u www-data php8.1 /var/www/cloud.uruk/public_html/occ analytics:load 12'
SOFT -GIT SERVER-¶
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://repo.charm.sh/apt/gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/charm.gpg
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/charm.gpg] https://repo.charm.sh/apt/ * *" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/charm.list
sudo apt update && sudo apt install soft-serve
Soft-Serve¶
Serve
Add new user in the server
ssh gitdowa user create ambagasdowa
ssh gitdowa user add-pubkey ambagasdowa `echo /usr/bin/cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub`
ssh gitdowa user create ambagasdowa '-k "`echo /usr/bin/cat .ssh/id_ed25519.pub`"'
Script for automate ssh commands
sshpass -p `/usr/bin/cat ~/credentials/db/baizabal.xyz/pw` runoverssh ambagasdowa "cd ~/gitlab/documents && ls" baizabal.xyz
Also works for rsync
sshpass -p `/usr/bin/cat ~/credentials/db/baizabal.xyz/pw` rsync -axPz ambagasdowa@baizabal.xyz:/var/www/cloud/public_html/data/username/files/ /media/backup/
Awk¶
Examples :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
curl -s https://hjg.com.ar/vocbib/art/theme.html | pup --color 'cite text{}' > ~/Documents/cites.theme
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |
file cites.sort
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 | |
Note
- remove unicode char
U+00A0 NO-BREAK SPACE inside vim :
%s\%xa0/ /g
- remove unicode char
Complete the numerical cites -
set hlsenable highlight -/\d\+,search only number cites to completesort lines for search duplicates
sortremove with
%!uniq
OutFile cites.theme.sort
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 | |
1 | |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 | |
awk 'NR==FNR{ a[$3]=$1;b[$3]=$2;next } { print b[$1]$0}' cites_sort cites.theme.lookup | sort | pr -t4 -s"&" > cites.theme.tex
1&1Par 22,9&1&Lev 3,1&2&Jer 23,9-40&3&Ef 4,3
1&1Re 22,13-28&1&Num 25,12&2&Jer 29,11&3&Flm 3
1&1Re 2,33&1&Num 6,26&2&Jer 33,9&3&Flp 4,7
1&1Re 5,26&1&Prov 12,20&2&Jer 6.14&3&Gal 3,28
1&1Re 5,4&1&Prov 3,2&2&Mal 2,5&3&Gal 5,22
1&1Re 9,25&1&Sab 3,1ss&2&Miq 3,5&3&Heb 13,20
1&1Sa 1,17&2&Am 9,13&2&Miq 5,4&3&Rom 12,18
1&2Re 9,18&2&Dan 10,19&2&Nah 2,1&3&Rom 14,17
1&2Sa 18,29-32&2&Dan 3,98&2&Os 2,20...&3&Rom 16,20
1&2Sa 7,1&2&Ez 13,15s&2&Zac 8,12&3&Rom 5,1-5
1&Ecl 3,8&2&Ez 34,25-30&2&Zac 9,9s&3&Rom 8,6
1&Eclo 44,14&2&Ez 37,26&3&1Cor 7,15&3&Sant 3,18
1&Eclo 45,24&2&Is 11,1..&3&1Tes 5,23&4&Jn 14,27
1&Eclo 47,13&2&Is 2,2..&3&1Tes 5,3&4&Jn 16,33
1&Ex 21,34&2&Is 26,3&3&2Cor 13,11&4&Jn 20,19-23
1&Gen 15,15&2&Is 32,15-20&3&2Tim 2,22&4&Lc 10,5-9
1&Gen 25,8&2&Is 45,7&3&Act 10,36&4&Lc 12.51
1&Gen 26,29&2&Is 48,18.22&3&Act 12,20&4&Lc 14,32
1&Gen 43,27&2&Is 52,7&3&Act 15,23&4&Lc 17,26-36
1&Job 9,4&2&Is 53,5&3&Act 24,2&4&Lc 19,38
1&Jos 21,44&2&Is 55.12&3&Act 7,26&4&Lc 19,42
1&Jos 23,1&2&Is 57,18s&3&Act 9,31&4&Lc 2,14
1&Jos 9,15&2&Is 60,17&3&Ap 21,2&4&Lc 2,29
1&Jue 18,5s&2&Is 65,25&3&Ap 6,4&4&Lc 24,36
1&Jue 4,17&2&Is 66,12&3&Col 1,20&4&Lc 7,50
1&Jue 6,23-24&2&Is 9,5-6&3&Col 3,11-15&4&Lc 8,48 p
1&Jue 8,9&2&Jer 14,13&3&Ef 2,14-22&4&Mt 5,9
1&Lev 26,1-13&2&Jer 20,10
The result above can be appended in a tex file
Awk¶
Here’s an awk solution,
$ <span class="hljs-built_in">cat</span> > list
C1
C2
H3
H4
O5
$ <span class="hljs-built_in">cat</span> > order
5
3
1
2
4
$ awk <span class="hljs-string">'NR==FNR{a[FNR]=$1;next} {print a[$1]}'</span> list order
O5
H3
C1
C2
H4
Brief explanation,
NR==FNR{a[FNR]=$1;next}: set the$1for each record in list into the array elementa[FNR]print a[$1]: for$1in each record in the fileorder, print correspondinga[$1]. In this case, the order would be kept.
PUP¶
Scrape contabo prices¶1 | |
Scrapes contabo bare metal servers¶1 | |
Clean empty lines¶1 | |
Cloud VPS 1
€
4
50
/ month
4 vCPU Cores
6 GB RAM
100 GB NVMe
or 400 GB SSD
1 Snapshot
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 2
€
9
50
/ month
6 vCPU Cores
16 GB RAM
200 GB NVMe
or 400 GB SSD
2 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 3
€
14
00
/ month
8 vCPU Cores
24 GB RAM
300 GB NVMe
or 1.2 TB SSD
2 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 4
€
26
00
/ month
12 vCPU Cores
48 GB RAM
400 GB NVMe
or 1.6 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 5
€
33
50
/ month
16 vCPU Cores
64 GB RAM
500 GB NVMe
or 2 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 6
€
61
50
/ month
24 vCPU Cores
120 GB RAM
600 GB NVMe
or 2.4 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 1
€
4
50
/ month
4 vCPU Cores
6 GB RAM
100 GB NVMe
or 400 GB SSD
1 Snapshot
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 2
€
9
50
/ month
6 vCPU Cores
16 GB RAM
200 GB NVMe
or 400 GB SSD
2 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 3
€
14
00
/ month
8 vCPU Cores
24 GB RAM
300 GB NVMe
or 1.2 TB SSD
2 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 4
€
26
00
/ month
12 vCPU Cores
48 GB RAM
400 GB NVMe
or 1.6 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 5
€
33
50
/ month
16 vCPU Cores
64 GB RAM
500 GB NVMe
or 2 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
Cloud VPS 6
€
61
50
/ month
24 vCPU Cores
120 GB RAM
600 GB NVMe
or 2.4 TB SSD
3 Snapshots
32 TB Traffic*
Unlimited Incoming
------
curl -s https://www.google.com/finance/markets/currencies | pup --color 'li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.ZvmM7 , li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.YMlKec text{}' | pr -t2 -s":"
USD / MXN:16.9724
EUR / MXN:18.2655
JPY / MXN:0.1109
GBP / MXN:21.2970
AUD / MXN:11.2035
curl -s https://www.google.com/finance/markets/currencies | pup --color 'li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.ZvmM7 , li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.YMlKec text{}' | pr -t2 -s":" | jq -cR | jq -s .
[
"USD / MXN:16.9724",
"EUR / MXN:18.2655",
"JPY / MXN:0.1109",
"GBP / MXN:21.2970",
"AUD / MXN:11.2035"
]
curl -s https://www.google.com/finance/markets/currencies | pup --color 'li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.ZvmM7 , li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.YMlKec text{}' | pr -t2 -s":" | jq -Rs '{array:split("\n")|map(split(":")|{(.[0]):.[1]}?)}'
# OR
curl -s https://www.google.com/finance/markets/currencies | pup --color 'li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.ZvmM7 , li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.YMlKec text{}' | pr -t2 -s":" | jq -nR '{currency: (reduce inputs as $line ([]; . + [$line | split(":") | {(.[0]):.[1]}]))}'
Output¶{
"array": [
{
"USD / MXN": "16.9724"
},
{
"EUR / MXN": "18.2655"
},
{
"JPY / MXN": "0.1109"
},
{
"GBP / MXN": "21.2970"
},
{
"AUD / MXN": "11.2035"
}
]
}
input¶curl -s https://www.google.com/finance/markets/currencies | pup --color 'li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.ZvmM7 , li > a[href*="-MXN"] div.YMlKec text{}' | pr -t2 -s":" |jq -R -n -c '[inputs|split(":")|{(.[0]):.[1]}]'
output¶[{"USD / MXN":"16.9724"},{"EUR / MXN":"18.2655"},{"JPY / MXN":"0.1109"},{"GBP / MXN":"21.2970"},{"AUD / MXN":"11.2035"}]
Webdav¶
sudo wsgidav --host=192.168.1.1 --port=80 --root=/home/ambagasdowa/web/1603-SIP-1.0.1/ --auth=anonymous
How to install Wsgidav
Tftp¶
sudo ptftpd -p 69 -v -D end0 /home/ambagasdowa/ftp/cp69xx/
pipy¶
pypisearch scdbf
Automount¶
git clone https://github.com/raamsri/automount-usb.git
Certifica.jar¶
java -jar Certifica.jar
Half Life Clock
Firts install sox
sudo apt install sox
sudo apt install libsox-fmt-all
Next Download the script and sounds
wget https://calomel.org/half_life_talking_clock.bz2
Note
Download the
half_life_talking_clock.bz2file which is only 169 kilobytes. It contains the perl script and the wav files in a nice little bzipped, tarball.Untar and bzip decompress the file using “tar jxvf half_life_talking_clock.bz2”
cd into the script directory, “cd half_life_talking_clock”
execute the script “./half-life_clock.pl” to hear the current time.
NCHAT¶
Whatsapp and Telegram in a text mode user interface
To download the nchat application on a Debian/Ubuntu system, follow the following steps, or for other distributions, follow the guides on the github page at nchat
sudo apt install ccache cmake build-essential gperf help2man libreadline-dev libssl-dev libncurses-dev libncursesw5-dev ncurses-doc zlib1g-dev libsqlite3-dev libmagic-dev golang git
git clone https://github.com/d99kris/nchat.git
mkdir -p build && cd build && cmake .. && make -s
sudo make install
Golang¶
Download code¶wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.20.14.linux-amd64.tar.gz
in ~/.profile¶export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
go version
VNC¶
Keyboard¶
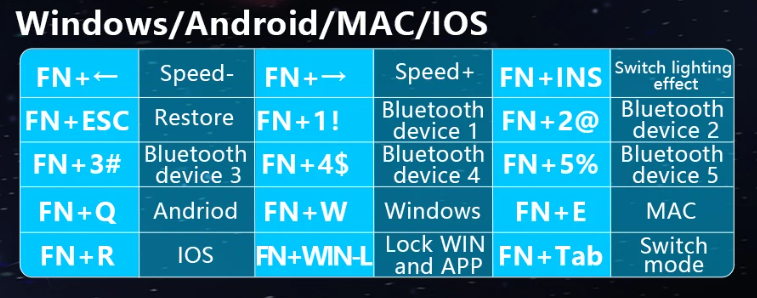
Aula Keyboard¶
product description:
Brand: |
AULA |
|---|---|
Model: |
F3287 |
Number of keys: |
87 keys |
Button service life: |
about 60 million times |
Connection method: |
Dual mode connection (Bluetooth/Wired) |
Full key no punch: |
Bluetooth supports 6 key no punch. Wired support N key no punch. |
Shaft body: |
green shaft/red shaft/brown shaft |
Product size: |
359x128.7x37.2+0.2mm |
Product weight: |
900g |
Instructions for use:
Fn key combination multimedia function can switch Android/Windows/MAC/IOS 4 systems. With low voltage alarm, the indicator light flashes to remind that the voltage is low and needs to be charged in time.
Independent function indicator, three light positions (from top to bottom): CAP and code indicator Display, charging and low voltage alarm indication, WIN indication.
The corresponding indicator light is on when it supports charging,and the corresponding indicator light is off when it is fully charged.
Self-service sleep function, if the device is not connected for 1 minute, the light will be off, and the keyboard will quickly enter deep sleep. Power saving. In wireless mode, if it is not used for about 3 minutes, the light will automatically turn off and the button will wake up.
Built-in 2000mA large-capacity lithium battery can be recharged cyclically, with power switch, environmental protection and energy saving, power saving and money saving, effectively prolonging battery life.
Precautions for use:
In Android/MAC/IOS, namely Fn+Q or E or R, F1~F12 are multimedia functions by default, and the combination with Fn is the original F1~F12 function. Composition is the multimedia function.
Press Fn+Esc to restore the factory default lighting mode, the original connected Bluetooth device will not be cleared.
The corresponding indicator light is on when supporting charging, and the corresponding light is off when fully charged.
Self-service sleep function, if the device is not connected for 1 minute, the light will be off, and the keyboard will quickly enter deep sleep, saving power. In wireless mode, the light will automatically turn off if you do not use it for about 3 minutes, and the button will wake up.
Built-in 2000mA large-capacity lithium battery can be recharged cyclically, with power switch, environmental protection and energy saving, saving Save money and effectively extend battery life.
Fn+Tab switch wired USB/Bluetooth mode. When the USB cable is not plugged in, switch to wired mode after 3S, the backlight will be off or press Fn+1 (or 2,3,4,5,), the Bluetooth pairing light will not flash.
Bluetooth mode can connect 5 devices, short press Fn+1 (or 2, 3., 4,5) to switch devices, right The code light flashes slowly, long press 1` (or 2,3,4,5) to match the code, the code light flashes quickly, the keyboard starts broadcasting ID,
The Bluetooth device to be connected (such as a computer, mobile phone or tablet, etc.) turns on Bluetooth and searches for “BLE Keyboard” This bluetooth keyboard is connected, the connection is successful and the code light is always on.
Automated Download PowerShell¶
Script for automated download and install connections script
Run Sudo command¶
sudo -- sh -c 'echo "ifconfig-push 10.44.45.151 255.255.255.0" >> ccd/consulta'
rename command¶
find . -depth -name "*.html" -exec sh -c 'f="{}"; mv -- "$f" "${f%.html}.php"' \;
For ce remove deb package ————————
sudo dpkg -r --force-depends "packagename"
XFS: Filesystem has duplicate UUID¶
How can I solve “_XFS Filesystem has duplicate UUID_” error message on my Linux server/Desktop?. If you get this error message in kernel _dmesg_ logs, it means you cannot mount your XFS partition. But don’t worry since we have a solution for you in this guide.
sudo mount -o rw,nouuid /dev/sda3 /mnt
1 2 3 4 | |
Monitoring a directory
watch --color -n0.1 tree -C --sort=ctime -trh --du /media/Black/Data/Roms/gc/{tmp,chd}
NFS¶
Install NFS client support¶
sudo apt install nfs-common
Test Block Device¶
time dd if=/dev/zero of=/home/ambagasdowa/remote-kukulkan/home/ambagasdowa/testfile bs=16k count=16384
Mount NFS device¶
for x in $(IFS=',';echo "White,Black,HGSDATA"); do mount -t nfs4 192.168.1.1:/media/"$x"; done
# OR if entry exists in fstab
for i in $(echo 'White,Black,HGSDATA' | tr ',' "\n" ) ; do mount /media/$i ; done
sudo mount -t nfs4 192.168.1.1:/media/HGSDATA /media/HGSDATA
Umount NFS
sudo umount /media/{White,Black,HGSDATA}
Restart NFS Service¶
exportfs -ra
sudo systemctl start nfs-kernel-server
OrangeUserRemove¶
At least for Debian 12 Bookworm running on Orange Pi 5 Plus: took me hours to find, but this worked for me: To disable the autologin, you need to edit the override.conf file under /usr/lib/systemd/system/getty@.service.d/.
Open the file in a text editor with root privileges. For example, if you’re using nano as your text editor, you would use the following command:
sudo nano /usr/lib/systemd/system/getty@.service.d/override.conf
Once the file is open, you should see the line that reads:
ExecStart=-/sbin/agetty –noissue –autologin orangepi %I $TERM
Edit this line to remove the –autologin orangepi option. The line should then read:
ExecStart=-/sbin/agetty –noissue %I $TERM
Save the changes and exit the text editor. In nano, you can do this by pressing Ctrl+O to save, and Ctrl+X to exit.
Finally, you need to reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes. You can do this with the following command:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
After these steps, the ‘orangepi’ user should no longer be logged in automatically. The next time you start your system, you should be prompted for a username and password.
sudo usermod -u 1000 ambagasdowa
sudo groupmod -g 1000 ambagasdowa
sudo vim /lib/systemd/system/getty@.service.d/override.conf
sudo vim /lib/systemd/system/serial-getty@.service.d/override.conf
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
"ps -aux | grep orangepi"
kill -9 <PID>
cat /etc/passwd | grep "ambagasdowa"
ambagasdowa:x:1000:1000:The Allmigthy:/home/ambagasdowa:/bin/bash
sudo find / -user 1003 -exec chgrp -h ambagasdowa {} \;
sudo find / -user 1003 -exec chgrp -h ambagasdowa {} \;
# Delete user
# ps aux | grep orangepi
# kill -9 <process ids of the orangepi user>
# userdel -f orangepi
find / -group 2000 -exec chgrp -h foo {} \;
find / -user 1005 -exec chown -h foo {} \;
Update Alternatives¶
Python¶
Add python 3.11
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.11 20
Check current config
sudo update-alternatives --config python
Fonts¶
For install local fonts copy font files to $HOME/.local/share/fonts/
then run:
HostnameCtl¶
How to determine if our computer is a desktop or laptop
Using hostnamectl With the chassis Option or Using dmidecode
sudo dmidecode -s chassis-type
In case we use a laptop, the output of the command may be “Laptop“, “Notebook“, “Portable“, “Hand held” or “Sub Notebook” depending on the manufacturer’s designation.
The other possible outputs of this command are “computer-laptop” for the laptop type, and “computer-vm” for the virtual machine type.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
Logs¶
logrotate
The safest mode to clean logs is using logrotate
logrotate -vf /etc/logrotate.conf
Cleaning /var/log/journal
journalctl --vacuum-time=10d
deleting :
sudo rm -rf /var/log/user.log
sudo rm -rf /var/log/syslog
sudo rm -rf /var/log/messages
systemctl restart syslog.service
In server lookup for highest log files and found debug and mail file ambagasdowa this files has up to 500 gb
The working command is :
truncate -s 0 /var/log/debug
truncate -s 0 /var/mail/ambagasdowa
FFMPEG¶
Extract Video¶
how to extract from 0 sec to 5 secs
ffmpeg -i kcho_y.mp4 -ss 00:00:00 -t 00:00:05 -c copy VideoClip.mp4
ffmpeg -i video.mp4 -ss 00:00:02 -t 00:00:03 -c:v copy -c:a copy trim-2.mp4
Grab the Desktop¶
ffmpeg -f x11grab -y -r 30 -s 1920x1080 -i :0.0 -vcodec huffyuv out.avi
Compress¶
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vcodec libx265 -crf 28 output.mp4
For telegram and other¶
ffmpeg -i out.avi -c:v libx264 -profile:v baseline -level 3.0 -pix_fmt yuv420p out.mp4
Note
This was really driving me nuts: It’s important that the file extension is “.mp4”. If you upload a video with “.m4v” extension you’ll not see a preview window and the video is opened in an external player. So here is my final command to reencode and resize a video and send it to the bot using curl:
ffmpeg -i input -an -c:v libx264 -crf 26 -vf scale=640:-1 out.mp4
curl -v -F chat_id=CHATID -F video=@out.mp4 -F caption=foobar https://api.telegram.org/bot<TOKEN>/sendVideo
NETWORK¶
Routes¶
with german gateaway
0.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
default via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1 proto kernel onlink
10.14.17.0/24 dev vmbr1 proto kernel scope link src 10.14.17.1 linkdown
10.44.45.0/24 dev tun1 proto kernel scope link src 10.44.45.224
128.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
173.212.200.183 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
192.168.1.0/24 dev eno1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.224
local internet gateaway
0.0.0.0/2 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
0.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
default via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1 proto kernel onlink
10.14.17.0/24 dev vmbr1 proto kernel scope link src 10.14.17.1 linkdown
10.44.45.0/24 dev tun1 proto kernel scope link src 10.44.45.224
64.0.0.0/2 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
128.0.0.0/2 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
128.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
173.212.200.183 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
192.0.0.0/2 via 192.168.1.254 dev eno1
192.168.1.0/24 dev eno1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.224
Toggle GW-Tunnel
sudo ip r add 0.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
sudo ip r add 128.0.0.0/1 via 10.44.45.1 dev tun1
Enable NAT
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Check DNS¶
#from local dns cache server (dnsmasq)
dig +short @127.0.0.1 A vgmrips.net
86.127.201.63
dig +short @1.1.1.3 A vgmrips.net
0.0.0.0
dig +short @1.1.1.1 A vgmrips.net
vampi.tech.
86.127.201.63
dig +short @192.168.1.1 A vgmrips.net
86.127.201.63
dig +short @1.1.1.1 A yahoo.com
98.137.11.163
74.6.231.21
98.137.11.164
74.6.143.25
74.6.231.20
74.6.143.26
Trace DNS query
dig +stats +trace baizabal.xyz
Querying NS records
Querying All Records
Reverse DNS Lookup
dig -x 208.118.235.148 +noall +answer
Check with drill
sudo apt install ldnsutils
drill baizabal.xyz | grep "Query time"
ImageMagick
convert to grayscale
mogrify -type Grayscale -path outPath -type Grayscale -gamma 1.8 -brightness-contrast +10 -normalize sourceImages/*.{jpg|png}
Note
Now as for your post… the complexity of the answer depends on the color transform involved. I’m no expert, but probably the easiest solution (based on what you seem to need) is to desaturate the image(s) and then increase contrast (and maybe brightness) using -brightness-contrast +5x25 (put in your own [brightness]x[contrast] values) or -normalize (automatic)
for png transparency can add
convert a.png -type Grayscale -transparent white b.png
Resize Image
convert -resize 20% source.png dest.jpg
proccess
Convert to pdf¶
convert '*'.jpg book.pdf
VPN Info¶
Active Certficates¶
sudo cat /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/pki/index.txt | sudo grep ^V | awk -F "/" '{print $2}' | awk -F "=" '{print $2}' | wc -l
Connected clients¶
sudo cat /var/log/openvpn/status.log | sudo sed -n '/OpenVPN CLIENT LIST/,/ROUTING TABLE/p' | tail -n+4 | sed "s/ROUTING TABLE//g";
Over SSH¶
sshpass -p remorte-ssh-pass ssh -t ambagasdowa@hypervpn "sshpass -p remote-sudo-pass sudo cat /tmp/report.csv" >> ~/gitdowa/baizabal.xyz/docs/Baizabal/source/_static/Downloads/UES/python/log.log
Note
Generally, your situation seems to predicate CCD, “client config dir”. CCD is a directory containing one file per connection profile. The file is tied to a unique client key, so that the key “johndoe” gets the profile specified in ccd/johndoe assigned when connecting. With this approach, you know which IP a specific client has. However, if you just want to list connected clients together with IPs, you can specify “status openvpn-status.log” in your config file. Then openvpn-status.log will contain an updated list of connected clients.
Connected Users¶
sshpass -p remote-password ssh -t ambagasdowa@hypervpn 'sshpass -p remote-password sudo cat /var/log/openvpn/status.log | sshpass -p remote-password sudo sed -n "/OpenVPN CLIENT LIST/,/ROUTING TABLE/p" | sshpass -p remote-password sudo tail -n+4 | sshpass -p remote-password sudo sed "s/ROUTING TABLE//g"' >> ~/list.csv && sc list.csv
Vpn remote listing¶
examples
sshpass -p `/usr/bin/cat $HOME/credentials/db/baizabal.xyz/pw` ssh -t baizabal.xyz '~/bin/log-vpn.sh' > ~/list.csv && sc list.csv
function lsvpn(){
if [ -z "$1" ]; then
echo "Usage lsvpn <server:baizabal.xyz|hypervisor>"
else
sshpass -p `/usr/bin/cat $HOME/credentials/db/baizabal.xyz/pw` ssh -t ambagasdowa@$1 '~/bin/log-vpn.sh' > ~/list.csv && sc list.csv
fi
}
alias lsvpn="lsvpn"
ordering the data with bash
echo "workstation,ip,a,b,datetime,tunnel,net,dt" > ~/ls.csv && ssh -t baizabal.xyz -- "~/bin/log-vpn.sh" >> ~/ls.csv && csvjson ~/ls.csv | jq
Output
[
{
"workstation": "kukulkan",
"ip": "201.108.183.68:49822",
"a": 9729919,
"b": 9737827,
"datetime": "2025-07-12T09:59:33",
"tunnel": "10.44.45.10",
"net": "201.108.183.68:49822",
"dt": "2025-07-12T09:59:33"
}
]
Remote Cloud¶
sudo -u www-data ; source ~/bash_alias ; find-tools -s -t pdf -p "search param" /var/www/cloud.gst/public_html/data/jose.sanchezf/files/Tesoreria/Comprobantes\ TBK/2025
ssh -t cloud.contabo -- "sudo -u www-data ; source /opt/find-tools.sh ; find-tools -s -t pdf -p search\ param /var/www/cloud.gst/public_html/data/jose.sanchezf/files/Tesoreria/Comprobantes\ TBK/2025"
Find and delete Files¶
find ./ -type f \( -iname \*.png -o -iname \*.jpeg -o -iname \*.pdf -o -iname \*.xlsx -o -iname \*.csv -o -iname \*.md \) -delete
rsync -axPz --exclude=*.pdf --exclude=*.jpg --exclude=*.png --exclude=*.csv --exclude=*.md /media/baizabal/Shareds/InvoicesTBK/Documents/Mar2025/ /media/baizabal/Shareds/InvoicesTBK/Documents/Apr2025/
Copying a Dir Structure with New Dir name¶
rsync --progress --stats -av -f"+ */" -f"- *" /media/baizabal/Shareds/InvoicesTBK/Documents/Apr2025/ /media/baizabal/Shareds/InvoicesTBK/Documents/May2025/
rsync Avoid failed verification¶
use --inplace option
or:
scp file.txt remote_username@10.10.0.2:/remote/directory
Iptables¶
Filter Network Traffic¶
with iftop
sudo iftop -P -n -N -m 10M -f 'port 3260'
Note
-P display ports -n no hostname lookup -N display ports not service names -m limit for bandwidth scale -f filter rule
with tcpdump:
tcpdump -i eth0 -s 1500 port 3306
Install zellig¶
How to change the root password¶
Method A (Using GRUB):
Turn on the computer.
While GRUB displays its screen, press ‘e’.
Edit the kernel line to include at the end: “init=/bin/dash” or your shell of preference but make sure it exists in the installation to be booted.
Press F10 to boot.
You will be presented a dreaded terminal. In that terminal you have root preveleges.
Since you have root privileges, you should be able to use passwd to change the root password.
Run the command and follow the prompts.
Reboot.
Method B (Using chroot):
Boot a Live CD on the computer you need to work on.
Open a terminal and become root.
Mount the root file system of the target installation.
Use chroot to become root on the target installation. If the mounted file system is mounted on /mnt/sda1, the command will be “chroot /mnt/sda1 /bin/bash”. You may need to use another shell emulator. Make sure you use one that exists on the the target installation.
Use passwd to change the root password on the target installation.
Exit the chroot with “exit” and unmount the target installation’s root file system.
Exit the Live Linux CD.
APT¶
force removal of a package
sudo dpkg -r --force-depends "packagename"
#or
sudo dpkg -r --force-depends "packagename-version"
Youtube Scraping¶
for get id use:
ytfzf --channel-link='https://www.youtube.com/@CodeHavox'
return:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCDGwW4yEjrsFGkY00y07u7Q
List Even and odd¶
Odd:
for i in {1..111} ;do (( $i%2 )) && echo $i ; done
Even:
for i in {2..111..2} ; do echo $i ; done
Nextcloud Migration¶
# Backup
mysqldump --single-transaction -h [server] -u [username] -p[password] [db_name] | gunzip -c > nextcloud-sqlbkp_`date +"%Y%m%d"`.bak.gzip
mysqldump --single-transaction -h [server] -u [username] -p[password] [db_name] | gzip > nextcloud-sqlbkp_`date +"%Y%m%d"`.bak.gz
# extract
gunzip < [dumpfile.sql.gz] | mysql -u [username] -p[password] [database_name]
gzcat foo.sql.gz | mysql -uroot -ppassword foo
mysqldump dbname | ssh root@remoteserver.com "mysql -D dbname"
# one command
mysqldump -u MYSQL_USER -p'MYSQL_PASSWORD' YOUR_DATABASE | gzip -c | ssh you@your_host 'cat > ~/backup.sql.gz'
mysqldump -u vivek -p'myPassWord' dbname | ssh vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz mysql -u backup -p'myPassword' dbname
# try
mysqldump -h db.example.com -u username -p --compress dbname | gzip --stdout > dbname.sql.gz
gunzip -c dbname.sql.gz | mysql dbname -u username -p
gzip dbname.sql | ssh user@remote "gunzip | mysql -h host -u username -p dbname"
mysqldump -u MYSQL_USER -p'MYSQL_PASSWORD' YOUR_DATABASE | gzip -c | ssh user@remote "gunzip | mysql -h host -u username -p dbname"
# Tested
mysqldump dbname | ssh root@remoteserver.com "mysql -D dbname"
#Test if works
mysqldump --single-transaction -h [server] -u [username] -p[password] [db_name] | gunzip -c | ssh user@remote "gunzip | mysql -h [host] -u [user] -p[pass] [dbname]"
mysqldump YOUR_DATABASE | gzip -c | ssh you@your_host 'cat > ~/backup.sql.gz && gunzip -c backup.sql.gz | mysql dbname'
mysqldump --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8mb4 -h localhost -u cloud.uruk -p'*******'' --databases nextcloud --add-drop-database | ssh ambagasdowa@192.200.99.53 "mysql -u root -p'*********' -D nextcloud"
# Section scripts
mysqldump --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8mb4 --routines --triggers --log-error=db_error.txt -h localhost -u root -p'***' --databases db_name --add-drop-database | gzip -c | ssh ambagasdowa@192.200.99.53 "cat > ~/backup_ediq.sql.gz"
ssh remote.example.com "mysqldump dbname | gzip -q -c -9" | gunzip -q | mysql dbname
### WORKING
ssh ambagasdowa@baizabal.xyz "mysqldump --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8mb4 --events --routines --triggers --log-error=db_error.txt -h localhost -u root -p'***' --databases nextcloud ttrss_uruk db_ediq2021 --add-drop-database | gzip -q -c -9 " | gunzip -q | mysql -u root -h localhost -p'***'
Mogrify¶
Crop image
mogrify -chop 0x20+0+0 -gravity South image.jpg -path outdir/
Commands Examples¶
Remove 45px from the bottom of a folder of images:
mogrify -chop 0x45+0+0 -gravity South \*.jpg or mogrify -crop +0-45+repage \*.jpg
Remove 45px from the right side of a folder of images:
mogrify -chop 45x0+0+0 -gravity East \*.jpg or mogrify -crop -45+0+repage \*.jpg
Resize images to be no larger than 1000px on any side:
mogrify -resize “1000x1000>” \*.jpg
Add 40px of white to the right side of the images:
mogrify -bordercolor white -border 40x0 -crop +40+0 +repage \*.jpg
Add 40px of black to the bottom of the images:
mogrify -bordercolor black -border 0x40 -crop +0+40 +repage \*.jpg
Add text (white, Arial Narrow, 16pt, centered) to the bottom of the images:
mogrify -font Arial-Narrow -pointsize 16 -fill white -gravity South-annotate 0x0+0+10 “Your text here.” \*.jpg
Add 40px wide white field to right side of image, then add text (black, Arial Narrow, 16pt, centered, vertical) in that field. (NB: the “\” is a line continuation character; just put everything in one line without the slash)
- ``mogrify -bordercolor white -border 40x0 -crop +40+0 +repage -rotate 90 -font Arial-Narrow -pointsize 16 -fill \
black -gravity South -annotate 0x0+0+10 “Copyright 2007, Ball State University. All rights reserved.” -rotate 270 *.jpg``
IMAGEMAGICK¶
Introduction to Imagemagick and some Basic Attributes
Some of the specifics of ImageMagick can be tricky to grasp when first starting, this section aims to explain some of the basic functions in order to take some of the edge off of the documentation.
Without understanding some basic concepts about the command line Imagemagick’s usefulness is extremely limited.
Chop¶
The first two numbers tell ImageMagick how much of the image to cut off of a picture. So, this:
200x300 x.JPG
will cut 200 pixels from the top of the image and 300 pixels from the right. The gravity function defines which corner to start from; by default gravity is set to start from the top-left of the picture (Northwest). Say you wanted to chop take 200 pixels from the bottom of the picture and 300 from the right side of the picture:
200x300 -gravity Southeast x.JPG
The optional x and y coordinates (200x300+x+y) will specify a point in the picture to start the chop so 200x300+100+600 would begin the crop 100 pixels down from the top and 300 pixels into the picture from the left. If these coordinates aren’t present the program assumes it should start in the corner.
Crop¶
The advantage to using the Crop feature is using it to modify a number of pictures. For example, on the quicktime VR movies it can be advantageous to crop all of the pictures in a set before sending them to VRWorx.
Here’s an example where I cropped all the pictures in a folder:
mogrify -crop 2716x1528+308+864 \*.JPG
The first two numbers tell imagemagick what dimensions the pictures should be and the last two numbers tell it the starting coordinates it should use. *.JPG makes the program run the crop on all files with the .JPG extension.
Follow the steps below to find any YouTube channel RSS Feed URL: 1. Go to the YouTube channel and copy the YouTube channel ID. This will be the text after / channel 2. Open the YouTube Channel RSS Feed URL link below 3. Paste the YouTube channel ID after channel_id= in the YouTube Channel RSS Feed URL
Follow the steps below to find any YouTube playlist RSS Feed URL: 1. Go to the YouTube playlist and copy the YouTube playlist ID. This will be the text after https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list= 2. Open the YouTube Playlist RSS Feed URL link below 3. Paste the YouTube playlist ID after playlist_id= in the YouTube Playlist RSS Feed URL
YouTube RSS Feed URLs: YouTube Channel RSS Feed URL: https://www.youtube.com/feeds/videos.xml?channel_id= YouTube Playlist RSS Feed URL: https://www.youtube.com/feeds/videos.xml?playlist_id=
backup vm with Clonezilla¶
ocs-sr -q2 -c -j2 -z9p -i 0 -sfsck -senc -p choose savedisk 2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz sda
partclone.ext4 -L /var/log/partclone.log -c -s /dev/sda1 --output - | zstdmt -c -3 --rsyncable > /home/partimag/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda1.ext4-ptcl-img.zst
#restore full image disk
ocs-sr -g auto -e1 auto -e2 -r -j2 -c -k0 -scr -p choose restoredisk disk.img nvme0n1
Clonezilla options¶
What do these restore options (-g auto, -t, -t1, -j1, -j2, -k, -k1, -j0, -r…) actually do? -g auto (default: checked): “Reinstall grub in client disk MBR (only if grub config exists)” This option will check if a grub boot loader exists in the MBR, if it exists, and a grub config file (/boot/grub/grub.cfg or /boot/grub/menu.lst) is found in restored partition(s), grub-install command will be run to reinstall grub boot loader. -t (default: unchecked): “Client does not restore the MBR” By default Clonezilla will clone or restore the MBR by dd, i.e. dd if=$IMAGE_DIR/$HARDDRIVE-mbr of=/dev/$HARDDRIVE bs=446 count=1 If option “-t” is checked, this dd command won’t be run. -t1 (default: unchecked): “Client restores the prebuilt MBR from syslinux (for Windows only)” If this option is checked, Clonezilla will dump a pre-build mbr file called mbr.bin (it’s from syslinux) to the destination disk by: cat mbr.bin > /dev/$HARDDRIVE -j1 (default: unchecked): “Write MBR (512 B) again after image is restored. Not OK for partition table differ from that of the image” In some cases, sfdisk uses different CHS values to create the partition table (due to different kernels have different CHS values of hard drive), and it will make the restore OS fail to boot. With this option checked, a command: dd if=$IMAGE_DIR/$HARDDRIVE-mbr of=/dev/$HARDDRIVE bs=446 count=1 will be run again after all the partitions are restored. -j2 (default: checked): “Clone the hidden data between MBR and 1st partition” Some vendor put some hidden data in the space between MBR and 1st partition. e.g. IBM thinkpad uses this for function key F11 to trigger the recovery action. Without this hidden data, F11 won’t work. -k (default: checked for restoredisk, and unchecked for restoreparts): “Do NOT create a partition table on the target disk” By default Clonezilla will create the partition table in the destination disk. If a partition table exists on the destination disk, and you do not want Clonezilla to overwrite it, you can check this option. -k1 (not default value): “Create partition table proportionally” By using this option, clonezilla will try to create the partition table on the destination disk proportionally. E.g. a 100 GB source disk with 2 partitions 20 GB and 80 GB, when -k1 option is checked, if the destination disk is 200 GB, the partitions created on the destination disk will be 40 GB and 160 GB. -j0 (default: unchecked): “Use dd to create partition” By default Clonezilla will use sfdisk to create the partition table. However, due to the CHS value might be different, the created partition table maybe won’t work for some OSes, and it makes the restored OS fail to boot. With this option checked, you can force Clonezilla to use dd to dump the binary image data from the source disk or image. -r (default: checked): “Try to resize the filesystem to fit partition size”. When this option is checked, the file system size on a partition will be tuned to fit the size of partition. E.g. on a 100 GB partition, the file system size might be only 60 GB (There is no need that the file system size must be equal to the partition size), with “-r” checked, clonezilla will try to use file system utils, e.g. “e2fsck” (for ext2/3/4), “resize_reiserfs” (for reiserfs), “ntfsresize” (for ntfs) to resize the file system size to fit the partition size. In this example, the file system size will be resized to be 100 GB. This option only deals with the file system size on a parttiion, so it’s nothing to do with partition size. It’s different from the option “-k1”, which deals with the partition size. -e1 auto (default: checked): “Automatically adjust filesystem geometry for a NTFS boot partition if exists”. When a NTFS exists, and its the boot loader partition for MS windows, clonezilla will try to use partclone.ntfsfixboot to set geometry and location parameters in NTFS filesystem, so it can boot. For more info, please check ntfsfixboot website. -e2 (default: checked): “sfdisk uses CHS of hard drive from EDD (for non-grub boot loader)”. When sfdisk creates the partition table on the destination disk, the CHS (cylinder, head, sector) number is read from EDD, not that from kernel. This is for non-grub boot loader, especially the boot loader of MS Windows. This option will not take effect if the boot loader on the destination disk is grub.
Clonezilla Log¶
Note
Starting /usr/sbin/ocs-sr at 2025-06-23 17:38:00 UTC… Start preparing device name cache files in /tmp/ocs-cache//… The file /proc/partitions remains the same. Skip generating disk(s) list file. Finding all partition(s)… Both /proc/partitions and blkid output do not change. Skip generating file system cache file related to the dev(s). *************************************************. Clonezilla image dir: /home/partimag *************************************************. Shutting down the Logical Volume Manager Finished Shutting down the Logical Volume Manager The image name is: src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz Selected device [sda] found! The selected devices: sda *************************************************. Activating the partition info in /proc… done! Selected device [sda] found! The selected devices: sda Searching for data/swap/extended partition(s)… Finding all disks and partitions.. Excluding busy partition…. Excluding linux raid member partition….. Unmounted partitions (including extended or swap): sda1 sda2 Collecting info… done! The data partition to be saved: sda1 sda2 Activating the partition info in /proc… done! Selected device [sda1] found! Selected device [sda2] found! The selected devices: sda1 sda2 Getting /dev/sda1 info… Getting /dev/sda2 info… *************************************************. The following step is to save the hard disk/partition(s) on this machine as an image: *************************************************. Machine: Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996) sda (1503GB_QEMU_HARDDISK__0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0) sda1 (953M_ext4(In_QEMU_HARDDISK_)_0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0) sda2 (1.4T_ext4(In_QEMU_HARDDISK_)_0QEMU_QEMU_HARDDISK_drive-scsi0) *************************************************. -> “/home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz”. Are you sure you want to continue? (y/n) y OK, let’s do it!! Shutting down the Logical Volume Manager Finished Shutting down the Logical Volume Manager Saving block devices info in /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/blkdev.list… Saving block devices attributes in /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/blkid.list… Checking the integrity of partition table in the disk /dev/sda… Reading the partition table for /dev/sda…RETVAL=0 *************************************************. The first partition of disk /dev/sda starts at 2048. Saving the hidden data between MBR (1st sector, i.e. 512 bytes) and 1st partition, which might be useful for some recovery tool, by: dd if=/dev/sda of=/home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda-hidden-data-after-mbr skip=1 bs=512 count=2047 2047+0 records in 2047+0 records out 1048064 bytes (1.0 MB, 1.0 MiB) copied, 1.75966 s, 596 kB/s *************************************************. done! Saving the MBR data for sda… 1+0 records in 1+0 records out 512 bytes copied, 0.152022 s, 3.4 kB/s *************************************************. *************************************************. Starting saving /dev/sda1 as /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda1.XXX… /dev/sda1 filesystem: ext4. *************************************************. Checking the disk space… *************************************************. Use partclone with zstdmt to save the image. Image file will not be split. *************************************************. If this action fails or hangs, check: * Is the disk full ? *************************************************. Running: partclone.ext4 -z 10485760 -N -L /var/log/partclone.log -c -s /dev/sda1 –output - | zstdmt -c -3 –rsyncable > /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda1.ext4-ptcl-img.zst 2> /tmp/img_out_err.AhSLzq Partclone fail, please check /var/log/partclone.log ! Checking the disk space… Failed to use partclone program to save or restore an image! Press “Enter” to continue…… *************************************************. Failed to save partition /dev/sda1. Press “Enter” to continue……
Saving hardware info by lshw… Saving DMI info… Saving PCI info… Saving S.M.A.R.T. data for the drive… cat: /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/parts: No such file or directory Saving OS info from the device… cat: /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/parts: No such file or directory Saving package info… *************************************************. *************************************************. Starting saving /dev/sda2 as /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda2.XXX… /dev/sda2 filesystem: ext4. *************************************************. Checking the disk space… *************************************************. Use partclone with zstdmt to save the image. Image file will not be split. *************************************************. If this action fails or hangs, check: * Is the disk full ? *************************************************. Running: partclone.ext4 -z 10485760 -N -L /var/log/partclone.log -c -s /dev/sda2 –output - | zstdmt -c -3 –rsyncable > /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz/sda2.ext4-ptcl-img.zst 2> /tmp/img_out_err.cE39y3 Partclone fail, please check /var/log/partclone.log ! Checking the disk space… Failed to use partclone program to save or restore an image! Press “Enter” to continue…… *************************************************. Failed to save partition /dev/sda2. Press “Enter” to continue……
End of saveparts job for image /home/partimag/src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz. *************************************************. *************************************************. This image was NOT saved correctly End of savedisk job for image src/2025-05-21-20-img-baizabal.xyz. Saving hardware info by lshw… Saving DMI info… Saving PCI info… Saving S.M.A.R.T. data for the drive… Saving OS info from the device… Saving package info… ************************************************* ************************************************* Checking if udevd rules have to be restored… This program is not started by Clonezilla server, so skip notifying it the job is done. Finished! Generating a tag file for this image… The mounted bitlocker device was not found. Skip unmounting it. Now syncing - flush filesystem buffers…
Mount with sshfs¶
sudo sshfs -o allow_other,idmap=user baizabal@utah.netdynamics24.com:/home/baizabal/gst/ /media/source/backup/
TSHARK¶
Capture packets from vpn¶tshark -i eth0 -d udp.port==1194,openvpn -f "port 1194"
PDF Book¶
scan the book
1.pdf 2.pdf etc
convert to GrayScale
mogrify -type Grayscale -path outPath -type Grayscale -gamma 1.8 -brightness-contrast +10 -normalize sourceImages/*.{jpg|png}
crop borders
# W x H + offset-top + offset-left
mogrify -chop 0x20+0+0 -gravity South image.jpg -path outdir/
- retouch with Gimp
Shift+P: perspective Shift+S: scale Shift+E:eraser Ctrl+Shift+E: export as Shift+E:eraser
Note
Inside a box text press Ctrl+Shift+U + hexcode or unicode for digraps and insert for example
«●» = Ctrl+Shift+U + A+B , Ctrl+Shift+U + `` 25cf`` , Ctrl+Shift+U + bb
on vim execute :digraphs ú,á,ñ,ª,é,ú,í,∅,∫,∬,∮,✓,“,»,
insert » press Ctrl+V + u00bb
or
insert » press Ctrl+K + >>
list digraps use cmd :dig or :digraps
retrieve info about a char use cmd
:ascii
on bash:
unicode 0x00bb
output:
U+00BB RIGHT-POINTING DOUBLE ANGLE QUOTATION MARK
UTF-8: c2 bb UTF-16BE: 00bb Decimal: » Octal: \0273
»
Category: Pf (Punctuation, Final quote); East Asian width: N (neutral)
Unicode block: 0080..00FF; Latin-1 Supplement
Bidi: ON (Other Neutrals)
Character is mirrored
Note
hbues => Herbert-Baizabal Universal Engineering Systems
HBUΣS
save pages as pdf
img2pdf $(find . -iname '*.png' | sort -V) -o ./document.pdf
Compress the pdf
gs \
-sDEVICE=pdfwrite \
-dCompatibilityLevel=1.4 \
-dPDFSETTINGS=/prepress \
-dNOPAUSE \
-dQUIET \
-dBATCH \
-sOutputFile=compressed_PDF_file.pdf \
input_PDF_file.pdf
Settings |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Has alower quality and smaller size. (72 dpi) |
|
Has a better quality, but has a slightly larger size (150 dpi) |
|
Output is of a higher size and quality (300 dpi) |
|
Output is of a printer type quality(300 dpi) |
|
Selects the output which is useful for multiple purposes. Can cause large PDFS. |
Script version¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 | |
Install Development tools on Debian 12
Restart NFS¶
sudo exportfs -ra && sudo systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
DMARC Records¶
You’ll need access to your domain’s DNS. Then you need to add the TXT Record at the Location/Target provided below.
TXT Record to Add in DNS¶
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:example@dmarcian.com;
Location/Target¶
_dmarc
So that the record is created at _dmarc.baizabal.xyz
Docx to Pdf¶
Convert docx documents to pdf
sudo apt-get install unoconv
find ./ -name "*.docx" -exec doc2pdf {} \;
Telmex Connection¶
Nombre del Producto: HG8145V5
Descripción: EchoLife HG8145V5 GPON Terminal (CLASS B+/PRODUCT ID:2150083933AGL4035007/CHIP:00000020200317)
Número de Serie: HWTCB316CBA2
Versión de hardware: 15ADA
Versión de software: V5R020C10S230A
Info de fabricación: 2150083933AGL4035007.C412
Nombre de la conecxion WAN
1_TR069_VOIP_INTERNET_R_VID_881
encapsulamiento: PPPoE
Modo Wan: Wan de ruta
Habilitar VLan : True
ID Vlan : 881
MRU: 1492
Usuario: 00259ELHWTCB316CBA2@prodigyweb.com.mx
Password: c572d4d0ddb4777e75beed3a79e09ca3f8d24f5e0359a625c6c82d5502e605d4
ID de VLAN multicast: 4001
deteccion de LCP: True
opc asociacion :lan x 4 ,ssid
obtencionIp:PPPoE
HabilitaNAT:True
ObtencionPreficjo:DHCP-PD
Bluetooth
sudo apt install bluetooth bluez-cups bluez-obexd bluez-meshd pulseaudio-module-bluetooth
Mopidy¶
Install dependencies
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
Install with pip¶
Install with pip¶pip install --upgrade mopidy
Install extensions
pip install Mopidy-MPD
pip install Mopidy-InternetArchive
pip install Mopidy-Jellyfin
Install from apt.mopidy.com
source: Docs mopidy
Add the archive’s GPG key:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo wget -q -O /etc/apt/keyrings/mopidy-archive-keyring.gpg https://apt.mopidy.com/mopidy.gpg
Add the APT repo to your package sources:
sudo wget -q -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mopidy.list https://apt.mopidy.com/bullseye.list
Install Mopidy and all dependencies:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install mopidy
Now, you’re ready to run Mopidy.
XSLTPROC¶
xml to csv
xsltproc ~/gitdowa/baizabal.xyz/docs/Baizabal/source/_static/Downloads/UES/xml/track.xslt /media/baizabal/Health/JAMB/acc/\{9618bc53-3fbf-433d-820c-0a3015e3c9a8\}.dia > /media/baizabal/Health/JAMB/acc/track.csv
install xmllint and xlsprocand xmlstarlet
Net¶
Close established TCP connection on Linux¶
using ss to check an terminate them
- ss:
-K,–kill forcibly close sockets, display what was closed
list them
ss -tp ‘( sport - :443 )’
or
ss –tcp src :443
terminate them
ss -K -tp ‘( sport - :443 )’
or
ss –kill –tcp src :443
Check Logs of systemd¶
journalctl -f -q --user-unit rpc.service | batcat --paging=never -l log -p
SAT Impuestos¶
Facturacion de Proveerores¶
Facturas de tipo Ingreso
Metodo de pago :
Pago en una sola exhibicion (PUE)Forma de pago Bancarizada
TransferenciaCFDI
Adquisicion de mercanciasyGastos en general
flowchart TB
A(SA de CV) -->|Link text| B(Transferencia)
B --> C{Decision}
C -->|One| D[Resico A]
C -->|Two| E[Resico B]
classDiagram
class BankAccount
BankAccount : (+) String owner
BankAccount : (+) Bigdecimal balance
BankAccount : (-) deposit(amount)
BankAccount : (-) withdrawal
erDiagram
CAR ||--o{ NAMED-DRIVER : allows
CAR {
string registrationNumber PK
string make
string model
string[] parts
}
PERSON ||--o{ NAMED-DRIVER : is
PERSON {
string driversLicense PK "The license #"
string(99) firstName "Only 99 characters are allowed"
string lastName
string phone UK
int age
}
NAMED-DRIVER {
string carRegistrationNumber PK, FK
string driverLicence PK, FK
}
MANUFACTURER only one to zero or more CAR : makesTEMARIO
Aplicación de la Resolución Miscelánea Fiscal en 2024
Uso obligatorio de la carta porte 3.0: – Contribuyentes obligados a emitirlo. – Entregas locales. – Campos de la versión 3.0. – Servicios de logística inversa, recolección o devolución para el traslado de los bienes y/o mercancías en autotransporte. – Plazo para seguir utilizando la versión 2.0 del complemento de carta porte.
Envío de la Contabilidad electrónica al SAT: – Contribuyentes obligados a llevar contabilidad. – Contribuyentes con la opción de utilizar MI CONTABILIDAD de MIS CUENTAS. – Contribuyentes con la opción de no enviar contabilidad.
Obligados a habilitar su buzón tributario en la página del SAT.
Régimen Simplificado de Confianza RESICO en 2024: – Tratamiento para 2024 de los contribuyentes que ya no puede tributar como RESICO. – Determinación de los pagos provisionales del RGL de los contribuyentes que tributaron en RESICO. – Obligaciones que debe de retomar el contribuyente que ya no puede tributar en el RESICO. – RESICO persona física que rebasan los $3,500,000, en algún mes del ejercicio 2023. – Personas morales del RESICO en liquidación. – Deducción de inventarios del RESICO persona moral. – Plazo para generar o renovar la e. firma.
Tablas del ISR para 2024 (anexo 8).
Revisando los cambios al Complemento de Pagos versión 2.0 revisión B, vigentes a partir del 15 de enero de 2024.
Cumplimiento de la obligación de presentar aviso de compensación.
Inscripción, reanudación y suspensión en el RFC de trabajadores.
Cédula de identificación fiscal y constancia de situación fiscal.
Saldos a favor de impuestos del ejercicio 2018 y anteriores fechas máximas para su compensación.
Clave 05 Sí objeto del impuesto, IVA crédito PODEBI del CFDI versión 4.0.
Reglas que se derogan.
Salarios mínimos de los trabajadores en 2024
Definición de salario mínimo: – Salario mínimo general. – Salario mínimo profesional.
Manejo del CFDI de trabajador de salario mínimo.
Ley de Ingresos de la Federación
Tasa de recargos y ejemplo de su determinación en el pago de impuestos.
Estímulos fiscales en 2024: – Diesel y biodiesel. – Concesión minera. – Libros periódicos y revistas. – Casetas.
Tasa de retención anual por intereses.
Ley del Seguro Social
Aportaciones voluntarias al Fondo Nacional de la Vivienda.
Aseguramiento voluntario al régimen obligatorio.
Definición: – Trabajador Independiente o por cuenta propia. – Unión civil. – Servicio de guardería.
Beneficios del taller en línea de ContadorMx
Sesión de preguntas y respuestas las cuales son contestadas completamente en vivo.
Conclusiones y recomendaciones.
Después del curso: soporte continuo a través de ContadorMx.
tmpcode:^Vy4M2jBTYrG1Wkt